Hong Kong Stock Exchange
The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong (SEHK, also known as Hong Kong Stock Exchange) is a stock exchange based in Hong Kong. It is the world's largest bourse in terms of market capitalization, surpassing Chicago-based CME. As of the end of 2020, it has 2,538 listed companies with a combined market capitalization of HK$47 trillion. It is reported as the fastest growing stock exchange in Asia.

The stock exchange is owned (through its subsidiary Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited) by Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (HKEX), a holding company that it also lists (SEHK: 388). The physical trading floor at Exchange Square was closed in October 2017.
Type - Stock exchange
Location - Central District, Hong Kong
Founded - 3 February 1891; 130 years ago (as Association of Stockbrokers in Hong Kong)
21 February 1914; 107 years ago (as Hong Kong Stock Exchange)
Owner - Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing
Key people
Nicolas Aguzin (CEO)
Laura Cha (Chairman)
Currency - Hong Kong dollar
No. of listings - 2,538 (2020)
Market cap - HK$47 trillion (2020)
Website - hkex.com.hk
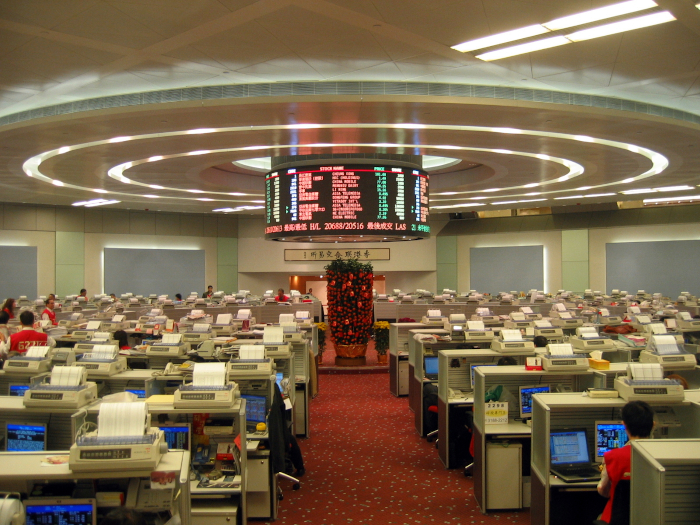

The now-defunct floor trading lobby in 2007
History
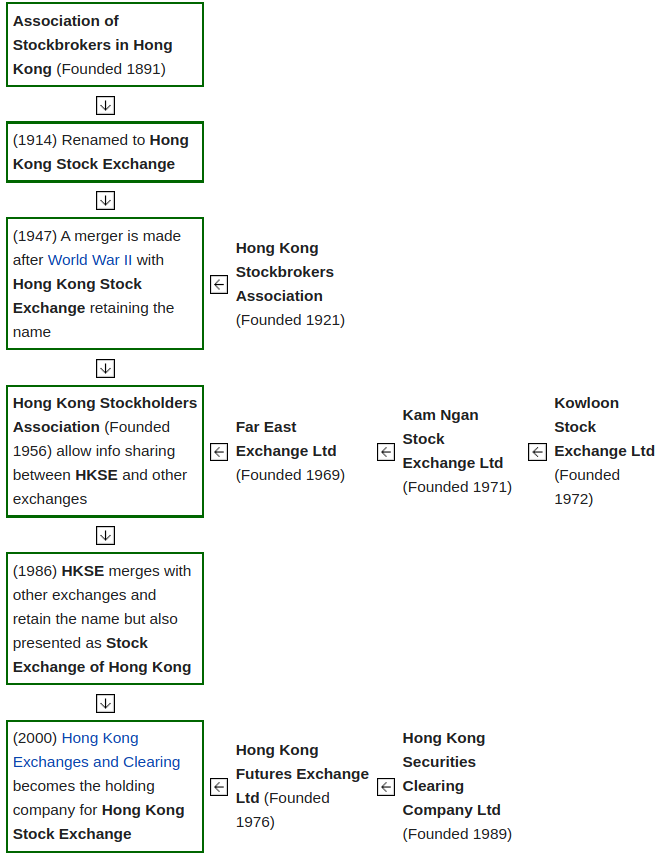
The Hong Kong securities market can be traced back to 1866, but the stock market was formally set up in 1891, when the Association of Stockbrokers in Hong Kong was established. It was renamed as The Hong Kong Stock Exchange in 1914.
By 1972, Hong Kong had four stock exchanges in operation. There were subsequent calls for the formation of a unified stock exchange. The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited was incorporated in 1980 and trading on the exchange finally commenced on 2 April 1986. Since 1986, a number of major developments have taken place. The 1987 market crash revealed flaws in the market and led to calls for a complete reform of the Hong Kong securities industry. This led to significant regulatory changes and infrastructural developments. As a result, the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) was set up in 1989 as the single statutory securities market regulator.
The market infrastructure was much improved[how?] with the introduction by the exchange of the Central Clearing and Settlement System (CCASS) in June 1992 and the Automatic Order Matching and Execution System (AMS) in November 1993. Since then, the framework of market rules and regulations, both exchange-administered or otherwise, have been undergoing continuing review and revision to meet changing market needs while ensuring effective market regulation.
The Exchange Listing Rules have been made more comprehensive, and other existing regulations have been improved or new regulations introduced to enhance market development and investor protection. Enhancements were also made to the system infrastructure, including the launch of off-floor trading terminals in brokers' offices in January 1996. The third generation of the trading system, AMS/3, will be launched in 2000. It will provide enhanced functionality and a platform for a straight-through transaction process.
In respect of market and product development, there is the listing of the first derivative warrant in February 1988, the listing of the first China-incorporated enterprise (H share) in July 1993; and the introduction of regulated short selling in January 1994 and stock options in September 1995. Furthermore, the exchange introduced the Growth Enterprise Market (GEM) in November 1999 to provide fundraising opportunities for growth companies of all sizes from all industries, and to promote the development of technology industries in the region.
According to the reform plan announced in March 1999, the Exchange, the Hong Kong Futures Exchange and their clearinghouses merged into a new holding company, the Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited.
Brief chronology
- On 2 April 1986, a new trading hall opened. At that time, a total of 249 companies were listed on the Exchange, total market capitalisation was HK$245 billion.
- 6 October 1986: Stock Exchange grand opening.
- October 1987: The Stock Exchange is closed for four days in an attempt to stop losses during Black Monday global equities market crash
- May 1988: The Ian Hay Davison Report, commissioned to investigate practices on the exchange in the lead-up to its closure, is released, resulting in significant market reforms - although many took years to finally implement
- On 24 June 1992, the Central Clearing and Settlement System (CCASS) is introduced
- On 15 July 1993, in the Tsingtao Brewery became the first Chinese enterprise to list its H shares on the exchange.
- On 1 November 1993, a new "Automatic Order Matching and Execution System", AMS/1, was introduced on the exchange; later, in January 1996, the second phase AMS/2 was introduced, becoming the basis of off-floor trading.
- On 12 November 1999, the Tracker Fund of Hong Kong, created by government intervention during the 1997 Asian financial crisis, had its introduction on the exchange.
- 25 November 1999, two companies were jointly listed on the newly created Growth Enterprise Market (GEM)
- On 6 March 2000, The Stock Exchange, Futures Exchange, and Hong Kong Securities Clearing Company all became wholly owned subsidiaries of HKEx, which was in turn listed on 27 June 2000.
- On 23 October 2000, AMS/3 was implemented on the exchange.
- On 27 October 2017, the floor trading lobby was closed due to the shift towards electronic trading. By 2014, the venue accounted for less than 1% of trade volume. The trading hall was renamed to Hong Kong Connect Hall and will be redeveloped as a museum, conference, and exhibition space to showcase Hong Kong's financial markets.
Exchange history and predecessors
Trading hours
The trading day consists of:
- A pre-opening auction session from 9:00 am to 9:30 am. The opening price of a security is reported shortly after 9:20 am.
- A morning continuous trading session from 09:30 am to 12:00 pm.
- An extended morning session from 12:00 noon to 1:00 pm, also referred to as the lunch break. Continuous trading proceeds in specifically designated securities (currently two ETFs, 4362 and 4363). Trading in other securities is not possible. However, previously placed orders in any securities can be cancelled from 1:00 pm onwards.
- An afternoon continuous trading session from 1:00 pm to 4:00 pm.
The closing price is reported as the median of five price snapshots taken from 3:59 to 4:00 pm every 15 seconds. In May 2008, the exchange also implemented a closing auction session to run from 4:00 pm to 4:10 pm, with a similar pricing mechanism as the opening auction; however, this resulted in significant fluctuations in the closing prices of stocks and suspicions of market manipulation. Initially, the exchange proposed limiting price fluctuations in the auction sessions to 2%; in the end, they removed the closing session entirely in March 2009.
Up until 2011, trading hours comprised a pre-opening auction from 9:30 AM to 9:50 AM, followed by continuous trading from 10:00 AM to 12:30 PM and 2:30 PM to 4:00 PM. The two-hour lunch break between the morning and afternoon sessions was the longest among the world's 20 major stock exchanges. A 2003 proposal to shorten the lunch break failed due to opposition from brokers. Another plan to shorten the lunch break to one hour was floated by the exchange in 2010; the morning session would then start earlier, run from 9:30 am to 12:00 pm, and the afternoon session from 1:00 pm to 4:00 pm, leaving the closing time the same as before. Justifications included bringing hours into line with China. Reactions from both brokers and the restaurant industry were mixed.
On 7 March 2011, the exchange extended its hours in the first of two phases. The morning session now ran from 9:30 am to 12:00 noon, followed by a ninety-minute lunch break, and an afternoon session from 1:30 pm to 4:00 pm. Index futures and options now began trading at 9:15 am, thirty minutes earlier than before, and closed at the same time as before, 4:15 pm. On 5 March 2012, the lunch break was cut to sixty minutes, with the afternoon session running from 1:00 pm to 4:00 pm.
Electronic trading
The exchange first introduced a computer-assisted trading system on 2 April 1986. In 1993 the exchange launched the "Automatic Order Matching and Execution System" (AMS), which was replaced by the third generation system (AMS/3) in October 2000.
Regulatory role
David Webb, independent non-executive director of the Exchange since 2003, has been arguing for a super regulatory authority to assume that role as regulator, as there is an inherent conflict between its commercial and regulatory roles. In the meantime, he argues for improved investor representation on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
In 2007, the uproar by smaller local stockbrokers over the decision by board of directors to cut minimum trading spreads for equities and warrants trading at between 25 HK cents and HK$2 caused the new board to vote to reverse the decision. The reforms were to be implemented in the first quarter, but was put back on the table following protests by brokers. Webb criticised the board for caving in to vested interests.
Trading characteristics
It is perfectly normal for Hong Kong stocks of even well-known companies to trade at prices that correspond to less than HK$4 a share. A Hong Kong stock would not be considered a penny stock unless its price was less than about HK$0.50.
Each stock has its own individual board lot size (an online broker will usually display this along with the stock price when you get a quote); purchases in amounts that are not multiples of the board lot size are done in a separate "odd lot market".
There is a close-in-price rule for limit orders, which must be within 24 ticks of the current price. Individual brokers may impose an even stricter rule; for instance, HSBC requires limit orders to be within 10 ticks of the current price. Broker support for triggered order types such as market-if-touched orders would allow placing orders further away, which would be sent to the exchange when the price condition was established.
Twenty largest stocks by market capitalisation
Source: HKEX, in billions of Hong Kong dollars, Data updated on 14 February 2018
- AIA: $6,764.32
- Tencent Holdings: $4,118.93
- Industrial and Commercial Bank of China: $2,877.98
- China Construction Bank: $2,167.39
- Bank of China: $1,803.12
- PetroChina: $1,715.53
- Agricultural Bank of China: $1,641.43
- HSBC Holdings: $1,629.79
- Ping An Insurance: $1,547.81
- China Mobile: $1,509.04
- China Merchants Bank: $991.75
- Bank of Communications: $985.55
- China Life Insurance Company: $844.57
- Postal Savings Bank of China: $676.41
- China National Offshore Oil Corporation: $492.91
- China Minsheng Bank: $420.11
- BOC Hong Kong (Holdings): $412.34
- China Pacific Insurance Company: $404.37
- CK Hutchison Holdings: $377.47
- CITIC Bank International: $367.82
Source: Wikipedia
Subscribe to free Financial-Portal.com newsletter
|




